What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum Computing is a computing model that factors in the laws of quantum mechanics.
According to CBINSIGHTS, Quantum computing is “the processing of information that’s represented by special quantum states”.

By including quantum phenomena like superposition and entanglement, quantum computers process information in a fundamentally different way to classical computers.
Key Definitions to understanding Quantum Computing
Quantum State
noun Physics.
Dictionary.com refers to a Quantum State as “the condition in which a physical system exists, usually described by a wave function or a set of quantum numbers.”
Superposition
Merriam-Webster states superposition is “the combination of two distinct physical phenomena of the same type (such as spin or wavelength) so that they coexist as part of the same event”.
Entanglement
ThoughtCo. States quantum entanglement describes “a situation where multiple particles are associated in such a way that measuring the quantum state of one particle also places constraints on the measurements of the other particles”.

Quantum Computing Vs Computing
via SwikBlog

Quantum Computers |
Classical Computers |
| Store and process information using qubits.
A qubit can represent 0, 1 or both simultaneously, represented by superposition.
Entanglement states then that when two qubits in a superposition correlate with one another, the state of one (0, 1 or both) depends on the other. |
Store and process information in bits.
Each bit represents either 0 or 1 (ON/OFF). |
| Analyse multiple routes simultaneously to solve a problem. | Analyse a route one at a time to solve a problem. |
| Can hold more information. | Can hold less information. |
| Can solve problems faster. | Can solve problems slower. |
| More efficient. | Less efficient. |
What is the future for Quantum Computing?
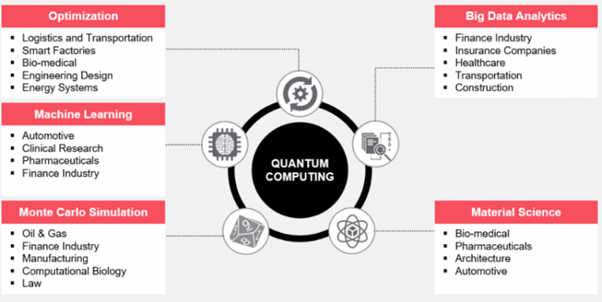
Via Futurbrice